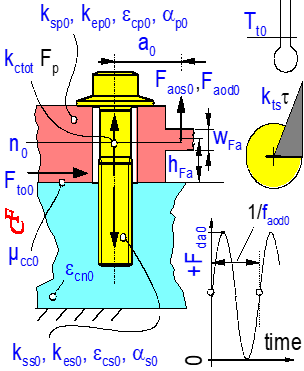
Simulations at tmax = time-saving + less costs
On the safe side, right from the start – with tmax simulations.
Reach your end product faster
with the help of simulations
Developing new products takes time, but it doesn't have to
Simulations using CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) make it possible to comprehensively assess concepts and designs in the early stages of a project so that, if possible, only one prototype needs to be built for testing. At tmax, the calculation methods used are verified in our in-house R&D laboratory through tests, so that after the successful testing and validation phase, approval and production can take place immediately.
The use of simulation of insulation concepts in the development process and on the test bench thus offers the following advantages:
- Time and cost savings, as no development loops are necessary.
- Early detection of a need for optimization, such as Hotspots on the cladding.
- Verification of fatigue resistance due to vibration.
- Ensuring the reach of required standards and regulations.
- The faster and more cost-efficient way to a production-ready insulation through true simultaneous engineering.
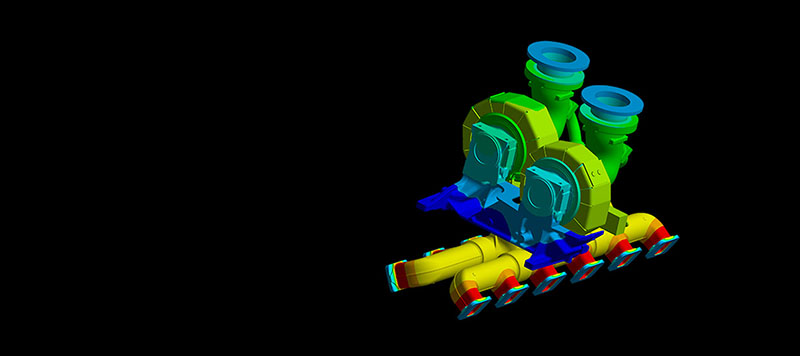
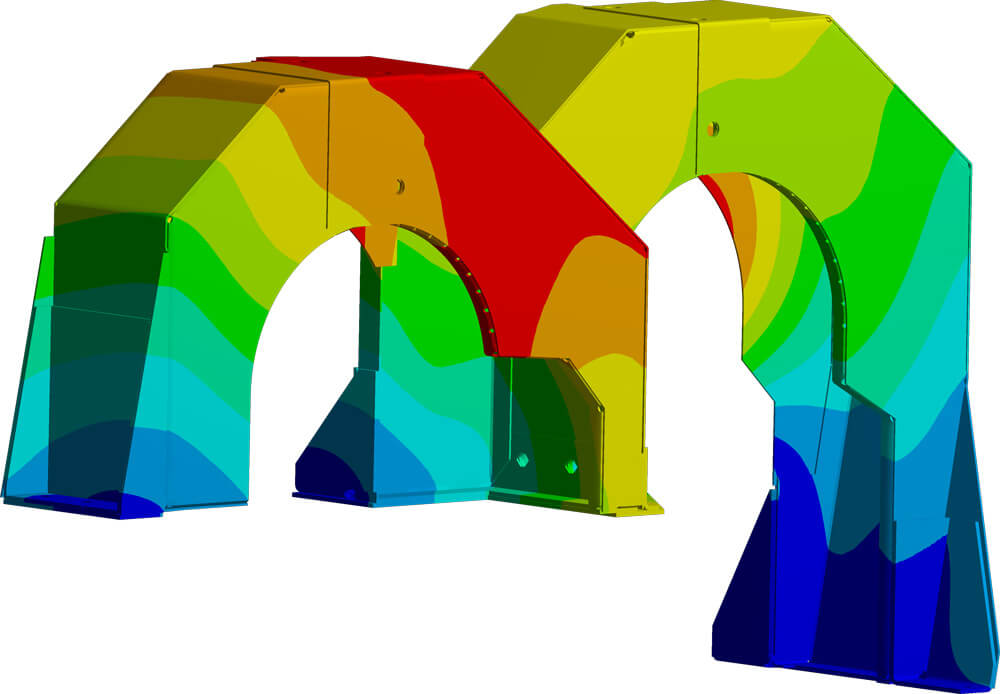
Structural analysis
Structural analysis can examine components and assemblies for their resistance to large forces that may act on the system from the outside. For example, when large waves hit a ship or a construction vehicle drives into a pothole, high accelerations occur. These in turn lead to large stresses on the components of the insulating cladding, which can cause damage if the design is not checked beforehand. Furthermore, it can be checked whether the accessibility of insulating components by service staff during maintenance work is guaranteed.
The range of services of structural analysis includes:
- Predicting the impact of collisions
- Predicting deformations of critical components
- Identification of highly stressed areas
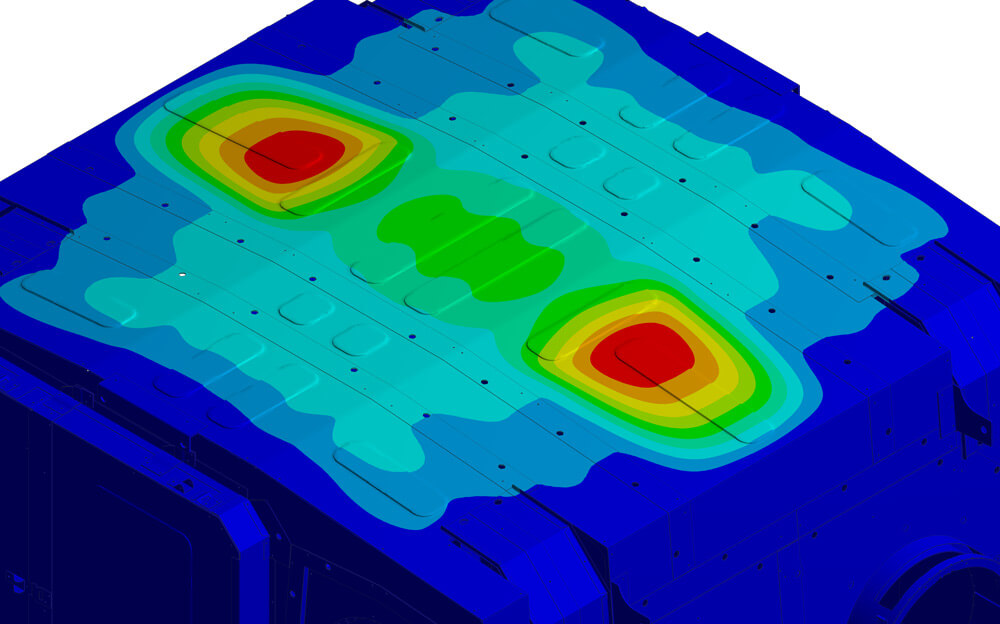
Vibration analysis
The vibration analysis examines the insulation cladding for its natural frequencies and the interaction between vibration excitation on the motor side, as well as the fatigue strength behavior of the insulation cladding.
- Determination of resonance frequencies
- Matching the harmonic motor excitation frequencies and natural frequencies of the cladding
- Avoidance of fatigue fractures due to High Cycle Fatigue
Temperature analysis
The temperature simulation determines surface temperatures of the insulation cladding to estimate whether the selected insulation configuration meets the required customer and legal specifications.
- Measurement of surface temperatures at any point of the model
- Determination of the temperature curve in the cross section
- Minimize prototyping and development loops through virtual prototype
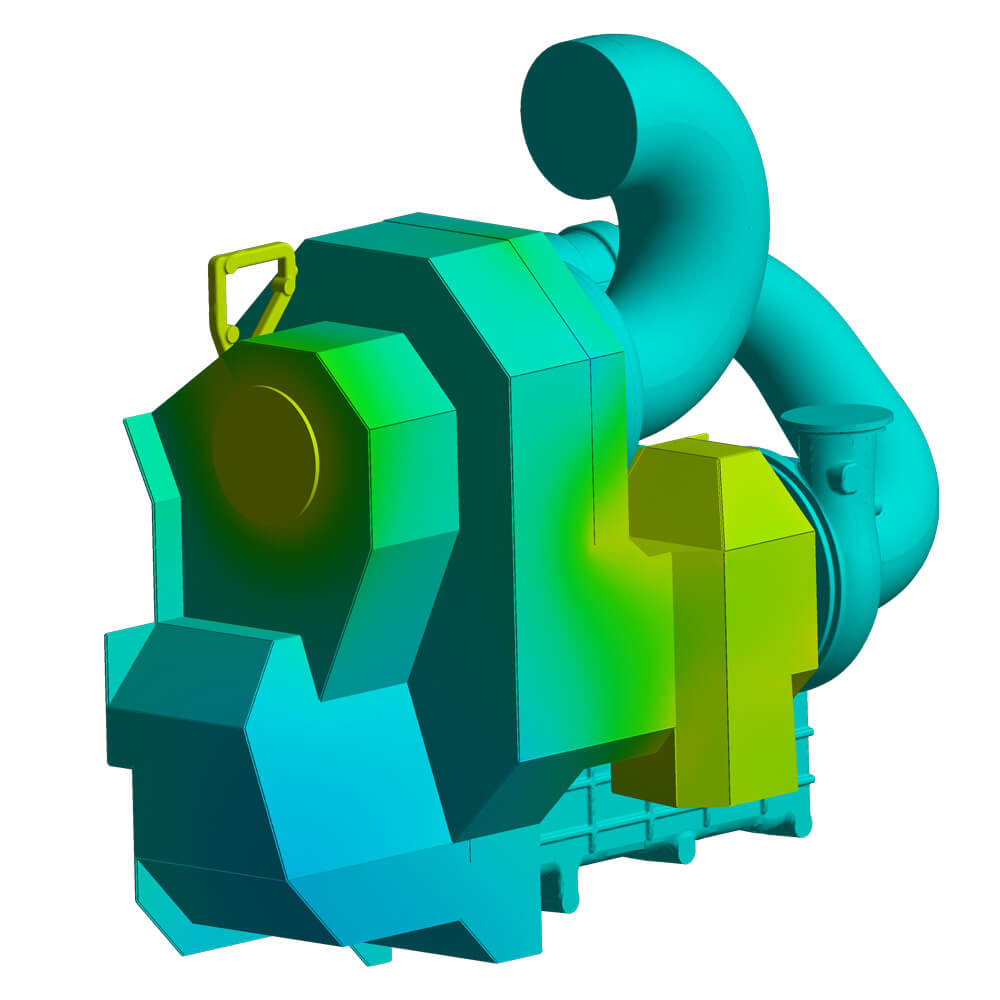

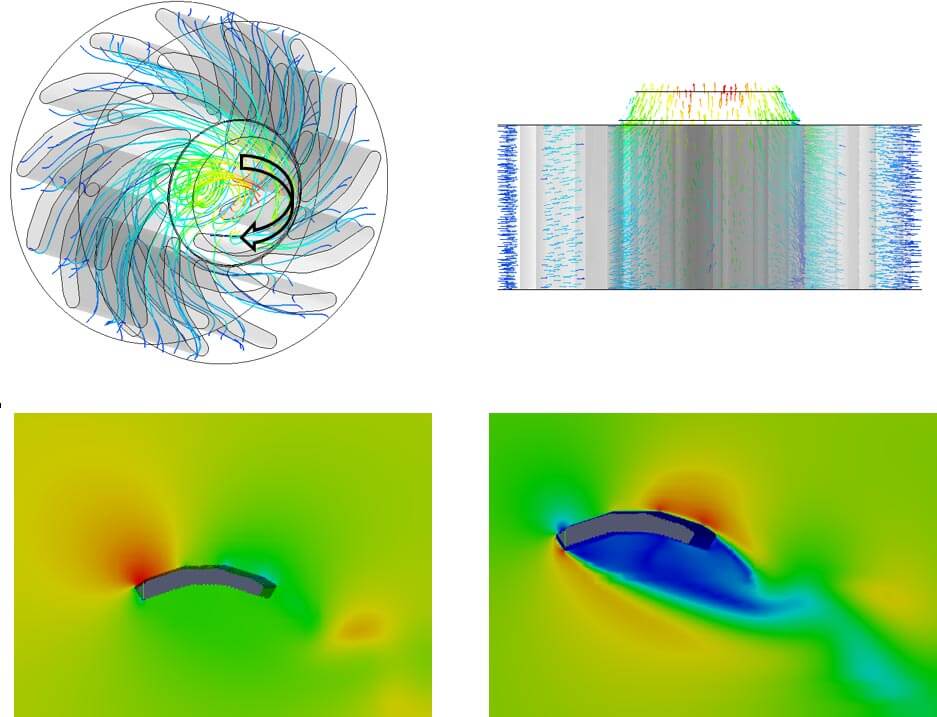
Flow simulation
The flow simulation evaluates components in terms of fluid dynamics, and consequently to minimize losses and reduce flow noise. Furthermore, it can predict what temperatures will occur at an insulating cladding under forced ventilation conditions.
- Conjugate Heat Transfer Analysis (heat transfer fluid ↔ solid)
- Time-dependent or steady-state flows
- Flow and noise optimization
Sheet metal forming simulation
Sheet metal forming simulation is used to predict how the material will behave during the forming process. It identifies areas of cracking, wrinkling or thinning, so that the part in question can be optimized accordingly. Punches and dies of the press tool can also be brought into the optimum shape even before production thanks to this simulation.
- Optimization of component and tool geometry
- Execution of feasibility studies
- Early prediction of component unit costs
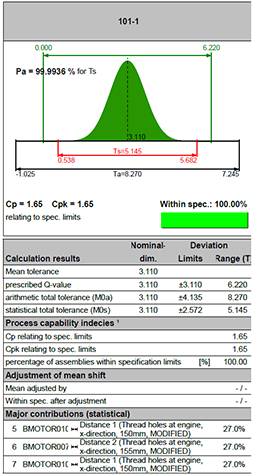
Statistical tolerance analysis
Tolerance analyses describe the effect of manufacturing errors in multi-stage processes. Within a production chain, there is only a limited error tolerance per component or work step. If too many errors accumulate, the component becomes unusable. The tolerance chain describes the defect tolerance beyond which the components no longer meet the higher-level quality requirements with regard to the customer.
Compared to arithmetic tolerance analysis, statistical tolerance analysis offers the advantage that it enables an economically sensible design of a product due to the statistical consideration of the tolerance chain, since small individual tolerances are avoided. This allows optimizations to be implemented quickly and costs to be reduced.
- Evaluation of results in the form of rework rate, degree of fulfillment and process parameters
- Arithmetic and statistical tolerance calculation – with temperature influences as well
- Integrated standards DIN ISO 268 and 2768 and DIN 16901/16742 are taken into account
Bolt calculation according to VDI 2230
The bolt verification calculation is used to secure the bolted joints at the connection points of the insulating cladding to the engine components, as well as to analyze the joints between the components of the cladding. The results are safety factors according to the specifications of the VDI (Association of German Engineers).
- Protection of bolted joints
- Safety against shearing, breakage, fatigue fracture, plasticization, separation, etc.
- In individual cases, further investigation through FEM simulation